Overview
SwatFlow Workflow is a Git workflow design that was published as an extension to the OneFlow branching model, an alternative to Gitflow. SwatFlow's main focus is to make the development and deployments processes as flexible as possible.
In this idea, SwatFlow allows developers to work both on active development and hotfixes at the same time without interfering with each other.
The only limitation becomes the number of developers working on the project!
SwatFlow is just a blueprint of how the branches and tags should be maintained and handled during the development and deployment process.
It uses the traditional feature, release and hotfix branches, with slightly modified behavior, but also introduces new branch types for added functionality, such as long-term support. One major change is the role of the 'master' branch, which has been reduced to a symbolic branch.
The purposes of the branches and tags will be described in the following sections.
Develop and Master Branches
In SwatFlow, develop is the core of everything, most feature branches and all release branches will branch out of it.
By default, develop will contain the history of all previous releases and will be the base of any future ones, but it doesn't contain the history of the whole repository as SwatFlow allows the update of any older release, no matter how old.
While develop takes a central role in this workflow, master becomes less important and an optional branch by having the sole purpose of pointing to the latest stable release.
This might be desired as any new clone of a git repository will, by default, check out the master branch.
Both develop and, if present, master, are indefinite branches which will exist forever in the repository.
Feature Branches
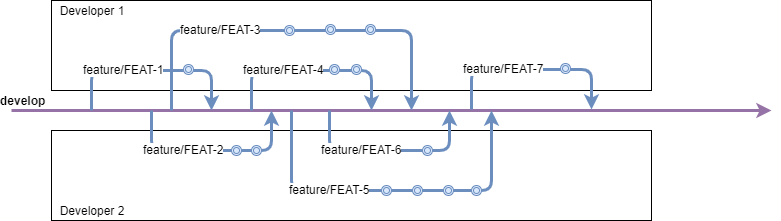
Similar to GitFlow and OneFlow, SwatFlow follows the Feature Branch Workflow, which entails doing any active development (new features, improvements, bugfixes, ...) on separate, independent 'feature/' branches.
Feature branches are created from develop and allow developers to work on their tasks, independent of one another.
Once the feature has been finished and has been approved by QA, a Pull-Request should be done to merge it into develop.
After the merge, the feature branch should be deleted as the branch is relevant during the development process, it is a short-lived branch.
To improve the model even further, the following actions are recommended:
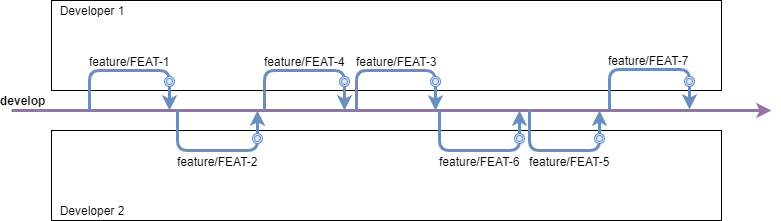
- Before doing a Pull-Request, developers should rebase onto develop to ensure no merge conflicts appear during the PR process.
This avoids pilling up merge issues when PR are accepted, providing a more swift development.
This is a requirements due to the way developers are able to work independent of one another, which means that developers can make changes to the same files without being aware of this. - Before doing a Pull-Request, once the developer has decided that the ticket has been finished, the commits on the feature branch should be squashed into a single one.
The advantage of this, is that, once merged, a feature branch is represented as a single commit on develop.
This provides a cleaner history and easier debugging.
With these improvements, the diagram above will look like this:
It can be seen that now, by rebasing and squashing, the history is considerably cleaner.
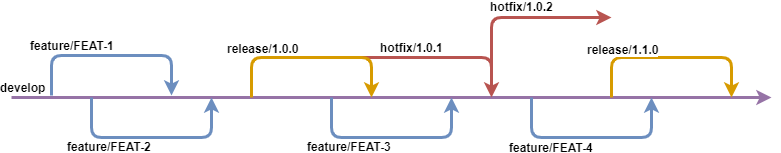
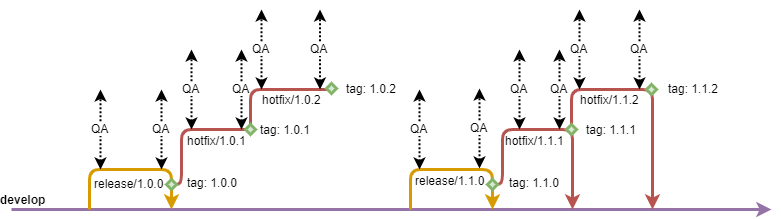
Release Branches
Once develop has accumulated an established amount of features, a new version should be released.
For this, a 'release/' branch will be created, which has the role of a snapshot of develop.
Once the release branch is created, the context of the release has been established and features can be continued to be merged into develop.
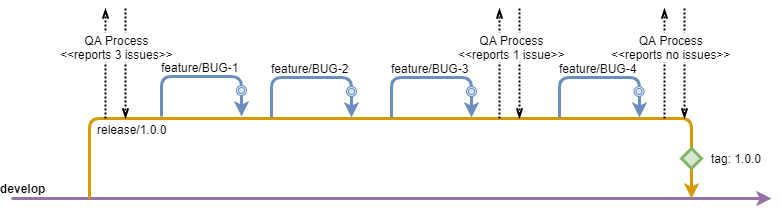
During the release process, the main focus will be QA.
Once the release is started, testing should be immediately started.
In the unfortunate case where QA detects an issue, developers will need to provide fixes.
For this, a feature branch should be branched from the release branch for each reported issue.
Similar to normal development, this allows for multiple developers to work independent of each other on the fixes.
As a result, all reported issues are resolved more efficiently, productivity is increased and release time can be considerably shortened.
At the end of the release process, once QA confirms that there are no more issues detected, a tag is created to denote the corresponding version and the release branch is merged into develop and deleted.
The release is merged into develop to make sure that all the changes on the release branch are also included on develop, and, inherently, in the next release.
Similar to the feature branches, release branches are short-lived and exist only during the release process itself.
Once the tag has been created and the branch is deleted, the release is finalized with no further changes allowed.
Any additional changes to the release will be done through hotfixes.
There can always only be, at any given time, one release branch relative to develop and each long term stability 'lts/' branch.
This means you can have multiple release branches, but they cannot have the same source branch (develop or 'lts/').
Hotfix Branches
Hotfix branches are similar in behavior to release branches, where QA is the main focus. Whenever an issue is reported by QA, feature branches are created to resolve them.
Where hotfixes differ to releases is in how they are created, finished and in their purpose.
A hotfix has the function of providing urgent fixes to existing releases, hence it is created directly from the release tag and, conditionally, merged into develop.
When the hotfix has been finished and approved by QA, a tag will be created, to mark the version. If the hotfix is done on the most recent release, then the hotfix also needs to be merged into develop to ensure that the fix is also included in the next release.
In case of a fix on an older release, the branch is simply deleted without any merge as the fix might not be relevant at all to more recent releases, for whom, hotfixes can also be created, if required.
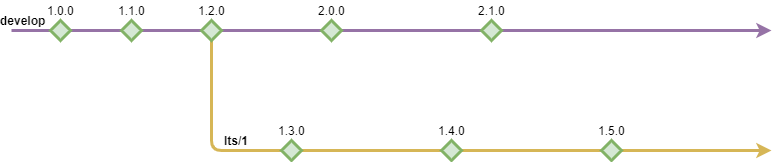
LTS Long Term Support Branches
There have been use-cases where the developed product got split into different version due to breaking changes, but both versions would need to be actively maintained. (ex. the Angular framework with AngularJS and Angular 2)
In such a case, there are 2 approaches, you can either fork the project into a second one and maintain the two versions as two completely separated projects, or you can maintain them in the same project.
For the second option, SwatFlow supports 'lts/' long term support branches, which allow active development on other branches than develop.
Long term support branches should only be maintained if actual development is planned, for maintaining a release and providing fixes, hotfixes should be able to satisfy any requirement.
Once the lts branch separation occurs, there should not be any more contact with develop or other lts branches.
Versioning
SwatFlow is fully compatible with GitVersion and is, actually, the recommended versioning system.
Maintaining the version of a single-project product
As seen above, whenever we finish a release or a hotfix, we tag the commit with a version (ex. 1.1.0, 1.3.2, ...).
Each tag represents a production-ready deployable version of the project.
This works fine when your product is maintained in a single git projects, but becomes more complex when it's spread among multiple ones.
Maintaining the version of a multi-project product
Regardless of having a single-project or multi-project product, each project should have an internal version.
In a single-project product, that internal project version can also be used as the product version, but this is not possible when multiple project are involved.
In this case, we need to have a separate product version. Similar to the project version, the product version can also be maintained through tags.
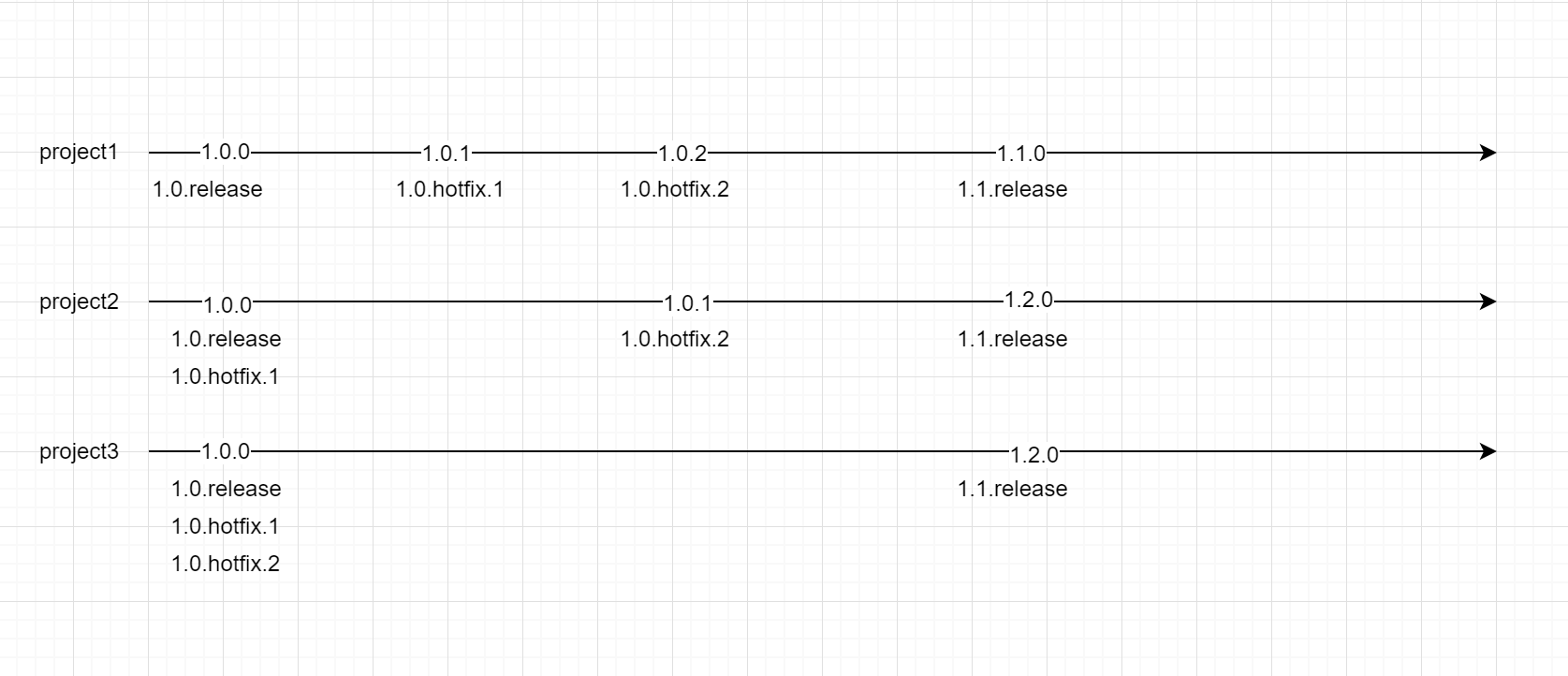
Below is an example for a product maintained in 3 different git projects:
The versions on the lines represent the corresponding project's internal release version, which is accesible through the corresponding tag. All the projects are tagged with the initial 1.0.0 version, which will be released as version 1.0.release of the product. A hotfix needs to be provided to 1.0.release, but the only required changes are in project1.
An additional hotfix is now required, so the next product version will be 1.0.hotfix.2.
It is decided that version 1.1.0 will be released. |